protein structure and protein folding
 |
| Protein structure |
Protein structure, We all have things that challenge us- and for me- it's folding. Sheets, towels, shirts- let’s simply say I invest in an exceedingly heap of anti-wrinkle laundry spray. superb invention. i do know folding within the schoolroom are often a strong thanks to organize ideas, but for me, it absolutely was the {particular} folding part that I attended bog down on. you'll consider folding as a convenience- of the way to require one thing and build it additional organized or condensed thus it doesn’t have to be compelled to take up the maximum amount house. this can be true.
however in biology, folding can even have tons to try to with operate. We’ve mentioned however superb proteins ar. they will play such a lot of roles. they will conjure channels, be an area of the structure, function enzymes for necessary biological processes, be involved protective the body...just to call some. We’ve additionally mentioned that you just ar creating proteins, all the time, in an exceedingly method called macromolecule synthesis.
however the conclusion of manufacturing an extended chain of amino acids doesn’t essentially equal a purposeful macromolecule. Protein structure There ar modifications to a macromolecule that always ought to happen so as for it to be purposeful. By modifications, we will mean several things. it'd be adding sure chemical teams, like phosphorylation---something to undoubtedly explore. however another necessary event to create a purposeful macromolecule is---believe it or not---folding. however before we have a tendency to get into folding, let’s quote form and why the form is thus necessary.
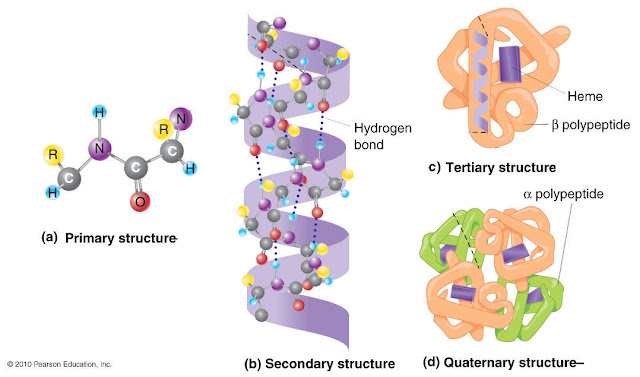
after we quote the method proteins ar sunray, we want to know totally different|the various} levels of macromolecule structure as a result of there ar other ways of folding that may happen within the different structural levels.
protein structure
 |
| protein structure |
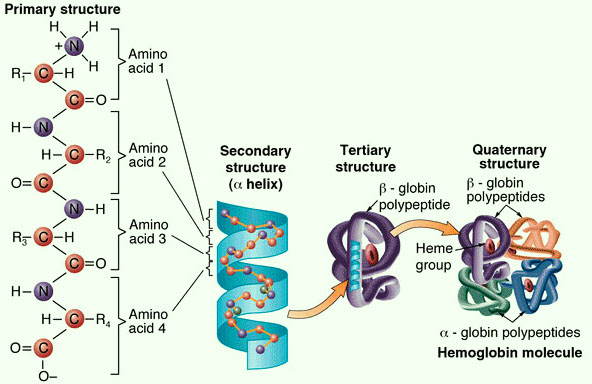
the primary level of macromolecule structure is that the primary structure. this can be the sequence of amino acids that conjure a macromolecule. Amino acids ar the monomer---which suggests that the building block---of a macromolecule. they're control along by amide bonds. In macromolecule synthesis, amino acids ar intercalary to make a peptide chain and proteins ar made from one or additional of those peptide chains. Genes, that ar made from deoxyribonucleic acid, confirm the order and variety of those amino acids.Protein structure
That sequence is essential to the protein’s structure and performance. Even one modification of associate organic compound has the potential to have an effect on a protein’s operate. we have a tendency to do wish to purpose out- every organic compound incorporates a carboxyl, associate radical, associated a R cluster- an R group is additionally known as a facet chain. thus although we've them drawn here sort of a chain of circles, notice that every of these circles we’re drawing is associate amino acid-like this.
Next, we have a tendency to pass on to the secondary Protein structure. Folding is actually progressing to begin to happen. In secondary structure, the sequence of amino acids that we have a tendency to mentioned within the primary Protein structure, will fold in numerous ways in which. the foremost common ar the alpha helix and also the beta-pleated sheet and which one in all these holdings the macromolecule will depends on the organic compound arrangement it's. each of those shapes ar due for the most part partly to atomic number 1 bonds.
Those atomic number 1 bonds will occur at specific areas of the protein’s amino acids. Specifically, these ar atomic number 1 bonds involving the backbone of the organic compound structure-we’re not specializing in the R teams straight away. On to tertiary structure. this can be viewing additional folding that happens within the 3D form of a purposeful macromolecule. And tons of this can be because of one thing we have a tendency to haven’t mentioned much…the R teams. additionally known as facet chains.
See, the radical and also the carboxyl ar usually customary elements of associate organic compound, though the R cluster found in amino acids will vary among completely different amino acids. That means, the R cluster will outline the organic compound and may build organic compound behave an explicit method. for instance, some R teams ar deliquescent. They like water. Some R teams ar hydrophobic. They don’t. And keep in mind that macromolecules contain several amino acids contain R teams and then different areas of the protein can, therefore, be compact supported those R teams. once folding goes on, amino acids with deliquescent R teams could hang around on the surface whereas hydrophobic R teams.
 |
| Protein structure |
Where ar they? they'll hang around within the within a part of the macromolecule. The 3D form is because of different interactions besides hydrophobic interactions. Ionic bonds, Van der Waals interactions, disulfide bonds, and chemical element bonds- all involving the R groups- additionally influence the folding occurring in tertiary structure. one thing to explore. currently once we’ve been talking a couple of macromolecule, we’ve been talking a couple of peptide chain that has been folded-up into a practical macromolecule.
however macromolecules will be made from one or a lot of peptide chains and in quaternary structure---you ar viewing a protein consisting of quite one peptide chain. every of those peptide chains will be a monetary unit and interactions between them like chemical element bonds or disulfide bonds will keep them along. Going back to the folding, i do know what you may be thinking. UN agency is doing this folding anyway? ar the proteins simply folding themselves? Well, the interactions mentioned like chemical element bonds and R cluster interactions ar occurring reckoning on the protein’s own amino acids.
One reason why organic compound sequences ar vital for macromolecule operate. however folding is much a lot of advanced than that, and there will be intermediate steps concerned once a macromolecule is folding. In fact, there’s a phrase you'll be able to search known as the protein-folding drawback to be told a lot of concerning the queries scientists still explore relating to biological process. analysis has shown that proteins usually have facilitate within the folding method.
Chaperonins, as an example, ar proteins which will facilitate with the folding method. they need nearly a barrel form. Proteins go in them, and therefore the chaperonin tends to possess associate degree setting that's ideal for the proteins’ folding. this may facilitate the macromolecule to be folded-up properly thus it’s practical. simply want I had one thing like that for my towels.
All of those interactions we have a tendency to mentioned within the primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary Protein structure ar preponderating for a mature macromolecule to possess its correct form thus it will do its operate. And that’s terribly relevant! There ar several diseases that ar associated with macromolecule misfolding.
One last item we have a tendency to haven’t mentioned: every macromolecule has a perfect setting for functioning which could embrace a particular temperature or pH scale vary. If the macromolecule is exposed to one thing outside of its ideal temperature or pH scale range- exposed to high heat for example- you'll be able to disrupt the interactions that we've talked concerning happening at the various structural levels. this may denature the macromolecule, that disrupts its form.
This prevents it from functioning properly. And reckoning on what caused it to be denaturised, typically you're busy with a lot of levels of macromolecule structure. Sometimes, it’s only one or 2 levels. typically denaturing a macromolecule could also be reversible. however in several different cases…it’s not. The setting that a macromolecule is indefinitely matters for its functioning. Protein structure




0 Comments
please, do not post spam links